Data replication is the act of keeping exact copies of your data in multiple locations, such as cloud environments, different servers or data centres. It’s a powerful way of improving your organisational resilience.
Multiple copies of the data in different locations means if one copy can’t be used, another copy can be accessed. These are live, real-time copies of data that allow for near-instant disaster recovery. This protects sensitive and functional company information, keeping operations ticking over if networks go down or hardware breaks.
How Data Replication Works

There are two ways this happens:
Synchronous replication: Data copies are backed up in real time as changes are made to the main system. This creates sharp consistency, but can lead to latency issues is networks are under pressure.
Asynchronous replication: The main system is updated first, and then the changes are sent to the data copies afterwards. This allows for speed and flexibility, although delays can occur in the copying process.
Which method is right for your organisation depends on the sensitivity of your data and how much delay your system can tolerate. Let’s look at the techniques you could use.
How is it Different from a Backup?
A data backup is an external storage of your data from a particular time. It can be used to restore the data if it’s deleted or lost. Replication works differently – if data is deleted from one server, it’ll then be deleted from all the servers. Replication is by no means a replacement for backups.
Data Replication Techniques
Full Replication
Full replication copies everything – every file, record and process. It is usually used during initial setup or major migrations. A full replication is resource-intensive, requiring substantial storage and bandwidth.
Incremental Replication
Incremental replication involves only copying over new or changed data from after the last replication event. It’s a faster update as there is less volume than a full replication. It’s commonly used for ongoing replication.
Log-Based Replication
This is mostly used in database environments. Changes are recorded in database logs which are then replicated to the other data copies. Data integrity is maintained, and the replication is efficient.
Snapshot Replication
An exact snapshot of data is made at a specific time. This snapshot is then replicated to the other data locations. This is often used in testing environments. Because changes aren’t in real time, it’s not a first choice for dynamic environments.
Transactional Replication
Individual transactions are tracked, recorded and replicated as they occur. This keeps all the copies closely aligned – you’ll find this method used in financial services environments or e-commerce setups.
Peer-to-Peer Replication
Peer-to-peer replication distributes data across multiple nodes. Each node is a source of data and a target for replication. This suits environments that need load balancing, like large-scale cloud networks.
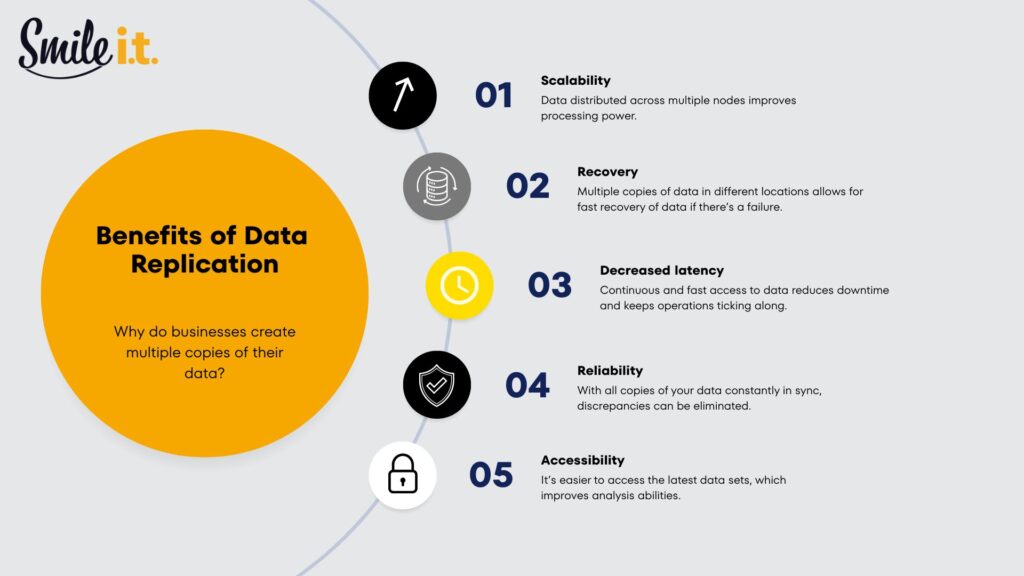
Benefits of Data Replication
Scalability
Replication allows organisations to expand their databases easily, while spreading workloads across multiple systems. As data increases, the user experience isn’t affected – the use of multiple nodes allows for more processing power.
Recovery
If something fails, replicated data gives you a fallback. Systems can be restored faster, and downtime is kept to a minimum.
Decreased Latency
Keeping data closer to users improves speed. This is especially useful for businesses operating across multiple locations.
Reliability
Multiple copies mean fewer single points of failure. If one system goes down, others can keep things running.
Accessibility
Replication makes it easier for teams, applications, and services to access the same data wherever they are working from.
Data Replication Use Cases
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
If your network environment goes down, having multiple copies of your data allows you to get back up and running. Operations switch across to the replicated data almost instantly.
Keeping Multiple Offices in Sync
Replication allows everyone to work from the same information even if a business has multiple offices in different parts of the world.
Safer Cloud Migrations
Replication plays a big role when moving systems to the cloud. Data can be copied gradually while systems remain live, allowing teams to test, validate, and transition without pulling the plug on the business.
Reporting Without Slowing Things Down
Analytics and reporting tools often work off replicated data. This keeps heavy reporting workloads away from live systems, so operational performance stays consistent while decision-makers still get the insights they need.
Testing and Development Without Risk
Development teams use replication to create test environments that closely match real systems. This allows changes, updates, and experiments to happen safely, without the risk of affecting live production data.
Data Replication Needs to Be Done Well

If it isn’t, systems can fall out of sync and the data will stop matching. This can create a whole lot of confusion as teams use new data in one instance and old data that hasn’t been updated in another.
Replication failures can occur too. Unmonitored copies may look fine, but in the background may have stopped updating.
Choosing the wrong method of data replication could also prove problematic. If the approach you land on isn’t the right fit for your network or workload, latency problems can occur. These can be very frustrating for end users trying to get on with their work.
Another major concern is data security. A high security approach needs to be taken to all data copies – it only takes one compromised copy to constitute an organisational data breach. You don’t want your replicated data to be an entry point to hackers.
What’s important to say is that data replication isn’t a one-time setup that you can then forget about. It requires proper design and ongoing monitoring to serve your business well over time.
Contact Smile IT with Your Data Replication Questions
Data replication can be an important tool for any Brisbane business. It can also be a liability if it’s not set up and monitored correctly. For the right advice and guidance, chat to a Smile IT team member. We’ve helped multiple businesses design and manage their data replication in a way that supports their business resilience and lays a platform for future growth.
When he’s not writing tech articles or turning IT startups into established and consistent managed service providers, Peter Drummond can be found kitesurfing on the Gold Coast or hanging out with his family!